As the Customer Success leader, you - and your team - are the company’s customer experts. Your CEO expects the CFO to know financial stats such as revenue and cash, the CRO to know pipeline and top prospects details, and the CMO to know MQLs and conversion rates. Similarly, as a Customer Success leader, you must understand who your current customers are, how your customers measure ROI and where there are risks and opportunities in your customer base.
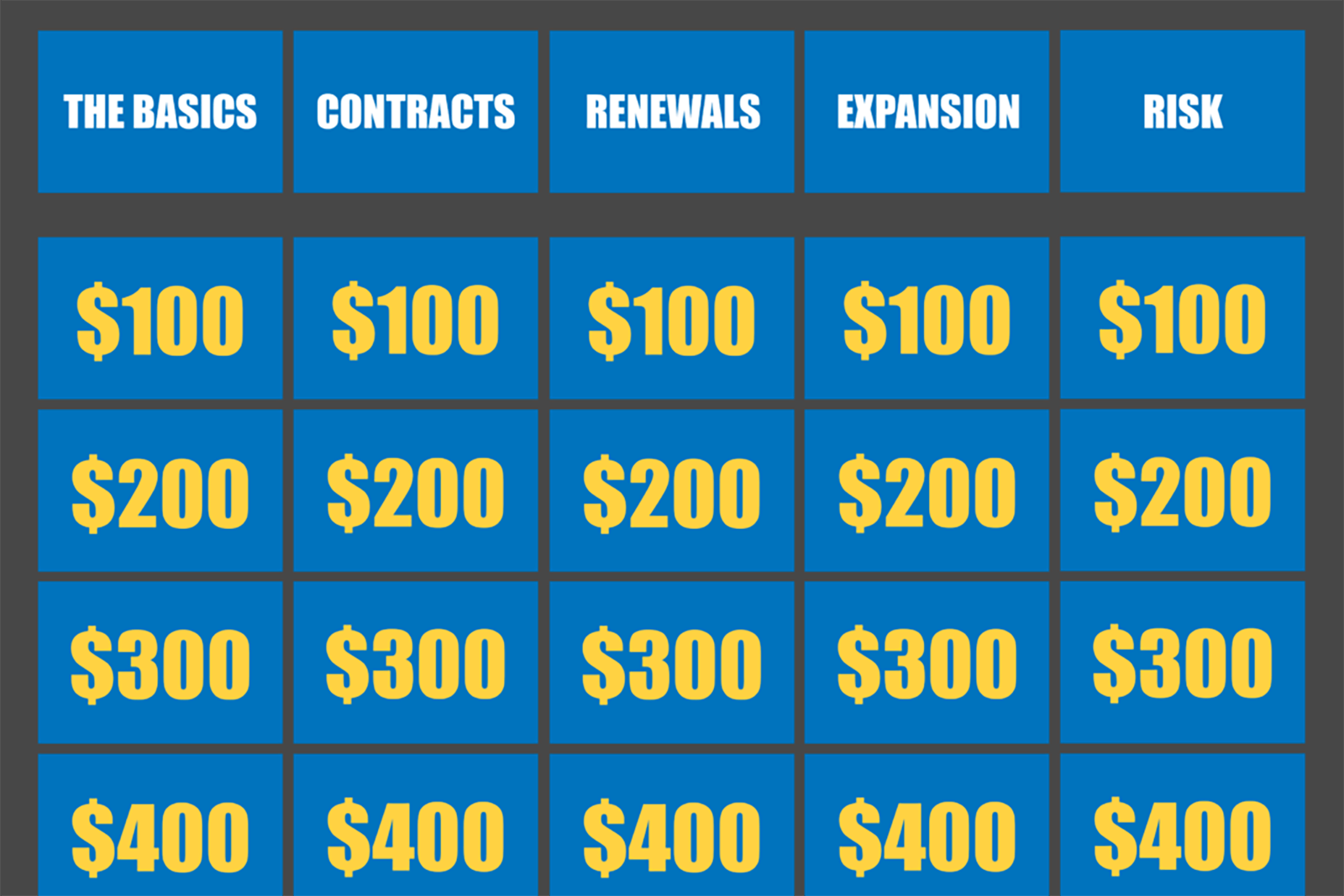
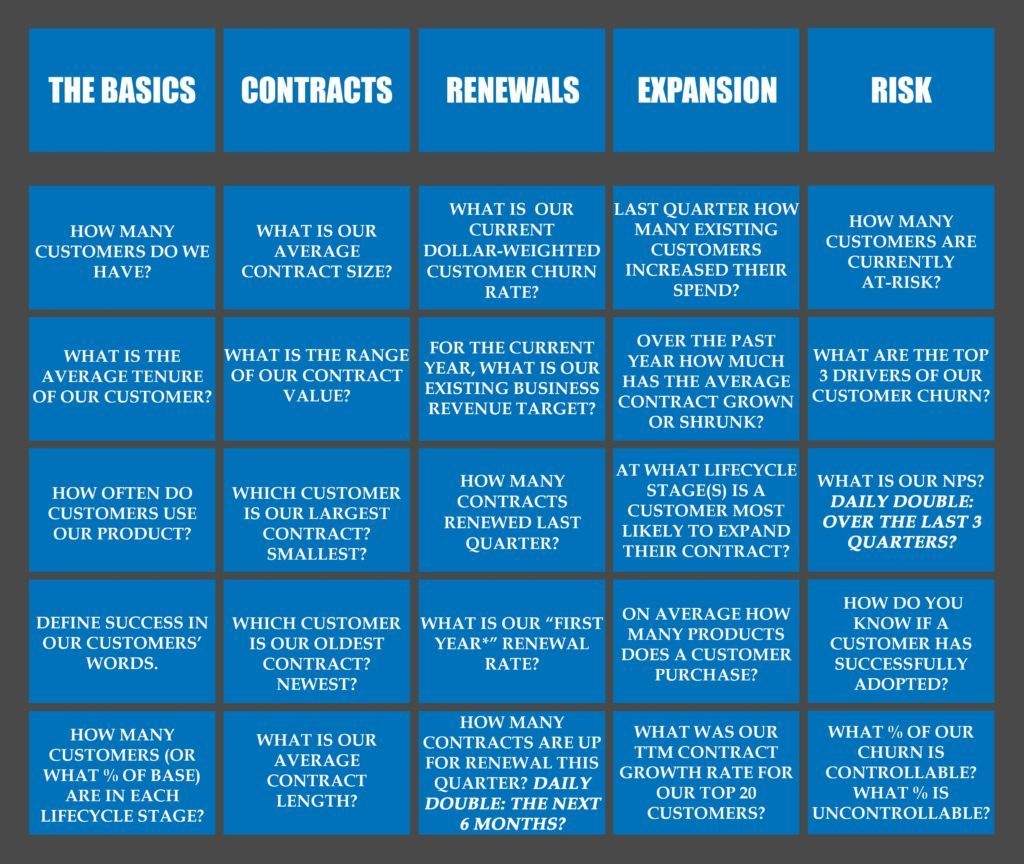
To test your knowledge play Insight’s Customer Success Jeopardy. Alternatively, build your own board and challenge your team in your next team meeting!
Footnotes:
Customer Lifecycle is the steps or phases that a customer goes through in interacting with a provider. The Customer Success team is involved once the contract has been signed. For example, the steps in a SaaS post-sales lifecycle could be Onboard, Adopt, Engage & Support, Renew, and Expand.
First year renewal rate is what percent of contracts renew at the end of the first contract term. For a customer with monthly contracts this occurs after the first month (i.e., month 1); for customers with annual contracts this occurs after month 12; for customers with three-year contracts this renewal occurs after month 36, etc.
TTM (Trailing Twelve Months): The last 12 month period for a financial metric. For example, the TTM renewal rate for the month of February would include all renewals from March of the prior year to February of the current year.
NPS: Net Promoter Score is a customer loyalty metric that assesses customer satisfaction. To learn how to calculate NPS, read “What is Net Promoter.”
Controllable churn are factors that a CSM or other part of the business can influence. An example is “customer did not see value” or “customer chose a competitor.”
Uncontrollable churn are factors which CSM intervention cannot change. Common examples of uncontrollable churn are M&A or bankruptcy.